Quick Start Tutorial
The following tutorial will guide you through setting up a SkyWalking OAP with BanyanDB as the storage backend using Docker Compose. It is a quick way to get started with BanyanDB if you are a SkyWalking user and want to try out BanyanDB.
Set up quickstart cluster with Showcase
Clone the showcase repository:
git clone https://github.com/apache/skywalking-showcase.git
cd skywalking-showcase
Start the showcase cluster:
make deploy.docker FEATURE_FLAGS=single-node,agent
You could find the details of the showcase cluster in the SkyWalking Showcase
Data presentation
Get into the SkyWalking UI
The UI can be accessed at http://localhost:9999.
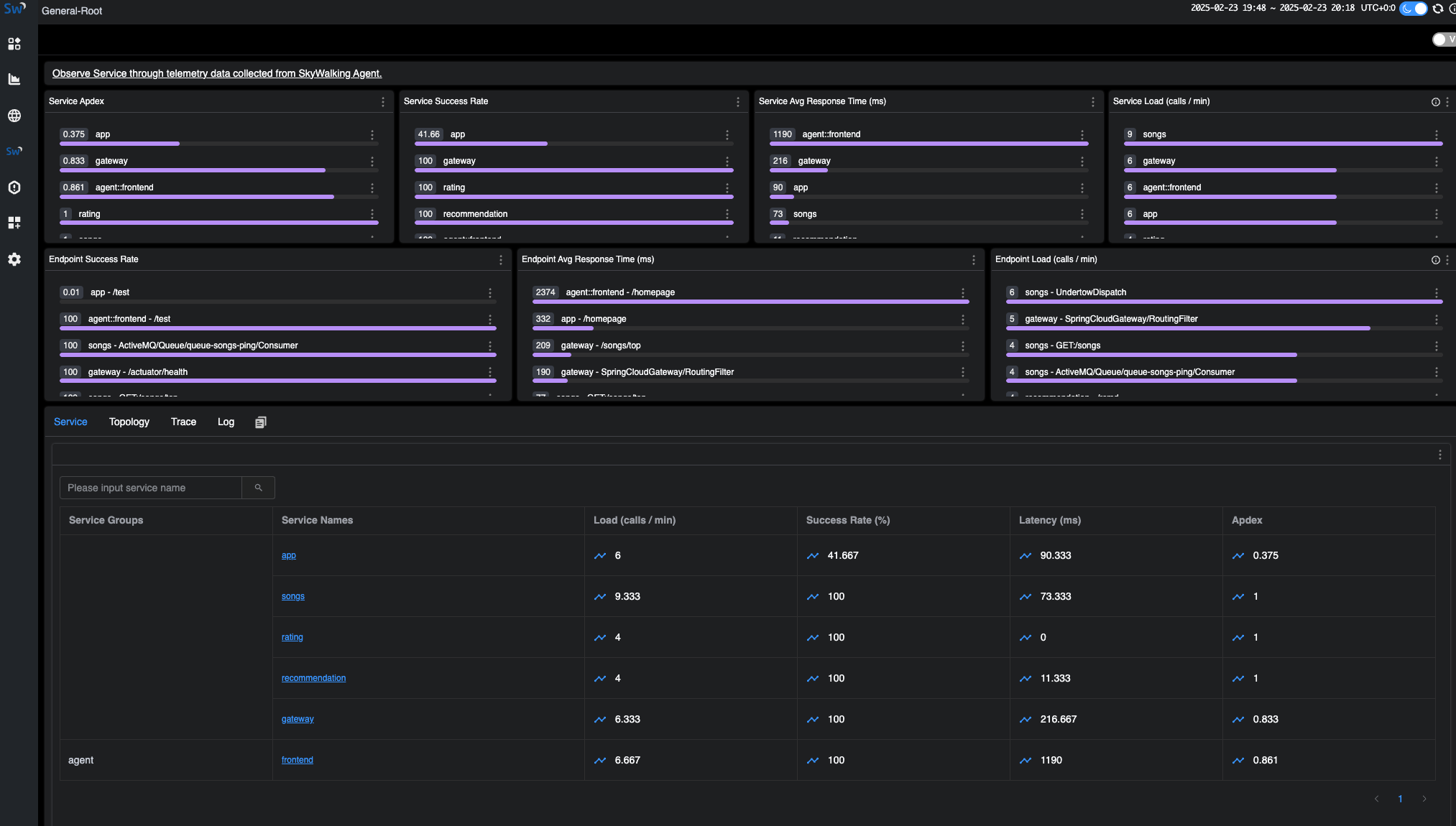
We can view the final presentation of the metrics/traces/logs/topology for the demo system on the UI dashboards.
The following image shows the General-Service service list in the SkyWalking UI:
Query the data in BanyanDB
If you interested in the raw data stored in BanyanDB, you can use the BanyanDB embedded UI or BanyanDB CLI(bydbctl) to query the data.
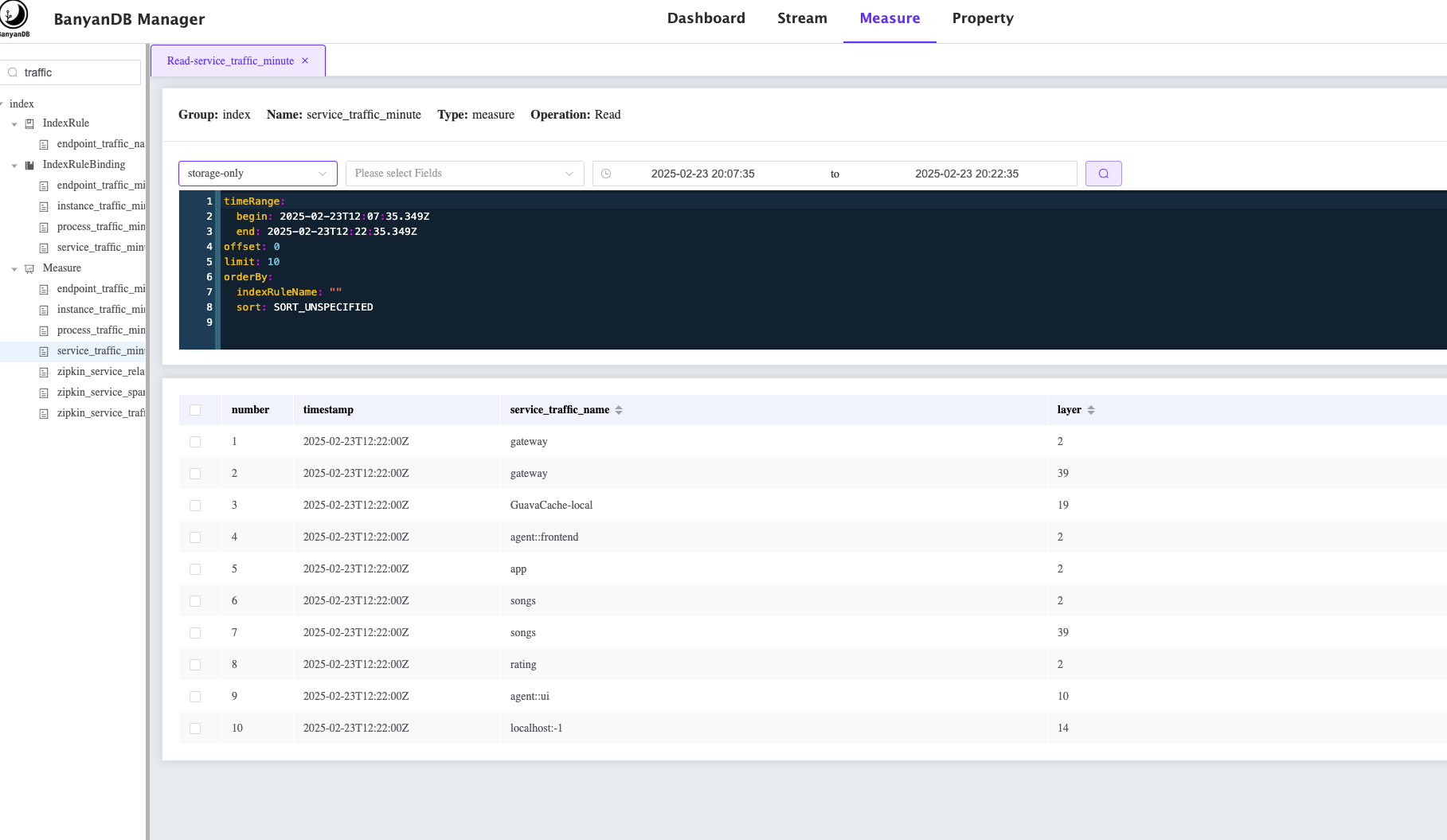
- BanyanDB embedded UI can be accessed at
http://localhost:17913. The following image shows how to query all the services from the BanyanDB:
- BanyanDB CLI(bydbctl) can be used to query the data from the command line.
bydbctl measure query -f - <<EOF
name: "service_traffic_minute"
groups: ["index"]
tagProjection:
tagFamilies:
- name: "default"
tags: ["service_id", "short_name","layer"]
EOF
We can see the following output:
dataPoints:
- fields: []
sid: "6694704579998440084"
tagFamilies:
- name: default
tags:
- key: service_id
value:
str:
value: Z2F0ZXdheQ==.1
- key: short_name
value:
str:
value: gateway
- key: layer
value:
int:
value: "2"
timestamp: "2025-02-23T12:36:00Z"
version: "9017360854805676"
- fields: []
sid: "2264252405119611112"
tagFamilies:
- name: default
tags:
- key: service_id
value:
str:
value: R3VhdmFDYWNoZS1sb2NhbA==.0
- key: short_name
value:
str:
value: GuavaCache-local
- key: layer
value:
int:
value: "19"
timestamp: "2025-02-23T12:36:00Z"
version: "9017360854808916"
- fields: []
sid: "7200167536615717650"
tagFamilies:
- name: default
tags:
- key: service_id
value:
str:
value: Z2F0ZXdheQ==.1
- key: short_name
value:
str:
value: gateway
- key: layer
value:
int:
value: "39"
timestamp: "2025-02-23T12:36:00Z"
version: "9017360854811805"
- fields: []
sid: "11101904457842605307"
tagFamilies:
- name: default
tags:
- key: service_id
value:
str:
value: YWdlbnQ6OmZyb250ZW5k.1
- key: short_name
value:
str:
value: frontend
- key: layer
value:
int:
value: "2"
timestamp: "2025-02-23T12:36:00Z"
version: "9017360854814505"
- fields: []
sid: "16886997253576549432"
tagFamilies:
- name: default
tags:
- key: service_id
value:
str:
value: c29uZ3M=.1
- key: short_name
value:
str:
value: songs
- key: layer
value:
int:
value: "2"
timestamp: "2025-02-23T12:36:00Z"
version: "9017360854817476"
- fields: []
sid: "3060777112302363794"
tagFamilies:
- name: default
tags:
- key: service_id
value:
str:
value: YXBw.1
- key: short_name
value:
str:
value: app
- key: layer
value:
int:
value: "2"
timestamp: "2025-02-23T12:36:00Z"
version: "9017360854820076"
- fields: []
sid: "3424504874722446951"
tagFamilies:
- name: default
tags:
- key: service_id
value:
str:
value: c29uZ3M=.1
- key: short_name
value:
str:
value: songs
- key: layer
value:
int:
value: "39"
timestamp: "2025-02-23T12:36:00Z"
version: "9017360854823045"
- fields: []
sid: "7814002932715409293"
tagFamilies:
- name: default
tags:
- key: service_id
value:
str:
value: cmF0aW5n.1
- key: short_name
value:
str:
value: rating
- key: layer
value:
int:
value: "2"
timestamp: "2025-02-23T12:36:00Z"
version: "9017360854827145"
- fields: []
sid: "4722671161330384377"
tagFamilies:
- name: default
tags:
- key: service_id
value:
str:
value: YWdlbnQ6OnVp.1
- key: short_name
value:
str:
value: ui
- key: layer
value:
int:
value: "10"
timestamp: "2025-02-23T12:36:00Z"
version: "9017360854831856"
- fields: []
sid: "5033399348250958164"
tagFamilies:
- name: default
tags:
- key: service_id
value:
str:
value: bG9jYWxob3N0Oi0x.0
- key: short_name
value:
str:
value: localhost:-1
- key: layer
value:
int:
value: "14"
timestamp: "2025-02-23T12:36:00Z"
version: "9017360854839325"
- fields: []
sid: "6492992516036642565"
tagFamilies:
- name: default
tags:
- key: service_id
value:
str:
value: MTcyLjE5LjAuNDo2MTYxNg==.0
- key: short_name
value:
str:
value: 172.19.0.4:61616
- key: layer
value:
int:
value: "15"
timestamp: "2025-02-23T12:36:00Z"
version: "9017360854846096"
- fields: []
sid: "724075540118355969"
tagFamilies:
- name: default
tags:
- key: service_id
value:
str:
value: cmVjb21tZW5kYXRpb24=.1
- key: short_name
value:
str:
value: recommendation
- key: layer
value:
int:
value: "2"
timestamp: "2025-02-23T12:36:00Z"
version: "9017360854850545"
trace: null